Note: this and the centernet paper share the same network name.
CenterNet is an improvement to CornerNet. Cornernet does not have high precision, as it’s sensitive to detect the boundary of the objects. CenterNet adds these things:
- Representing a proposal by using keypoints triplets (2 corners + 1 center), instead of a pair. More on that later.
- center pooling, which is just like Corner pooling, but now consider the whole image, summing max response in horizontal and vertical directions.
- cascade corner pooling. More on that later.
What is the center point used for
It’s basically used to filter out FPs + ging the model opportunities to explore visual patterns.
Specifically, we embed a heatmap for the center keypoints on the basis of CornerNet and predict the offsets of the center keypoints. Then, we use the method proposed in CornerNet to generate top-k bounding boxes. However, to effectively filter out the incorrect bounding boxes, we leverage the detected center keypoints and resort to the following procedure:
- Select top-k center keypoints according to their scores
- Use the corresponding offsets to remap these center keypoints to the input image
- Define a central region for each bounding box and check if thecentral region contains center keypoints. Note that the class labels of the checked center keypoints should be same as that of the bounding box
- If a center keypoint is detected in the central region, we will preserve the bounding box. The score of the bounding box will be replaced by the average scores of the three points, i.e., the top-left corner, the bottom-right corner and the center keypoint. If there are no center keypoints detected in its central region, the bounding box will be removed.
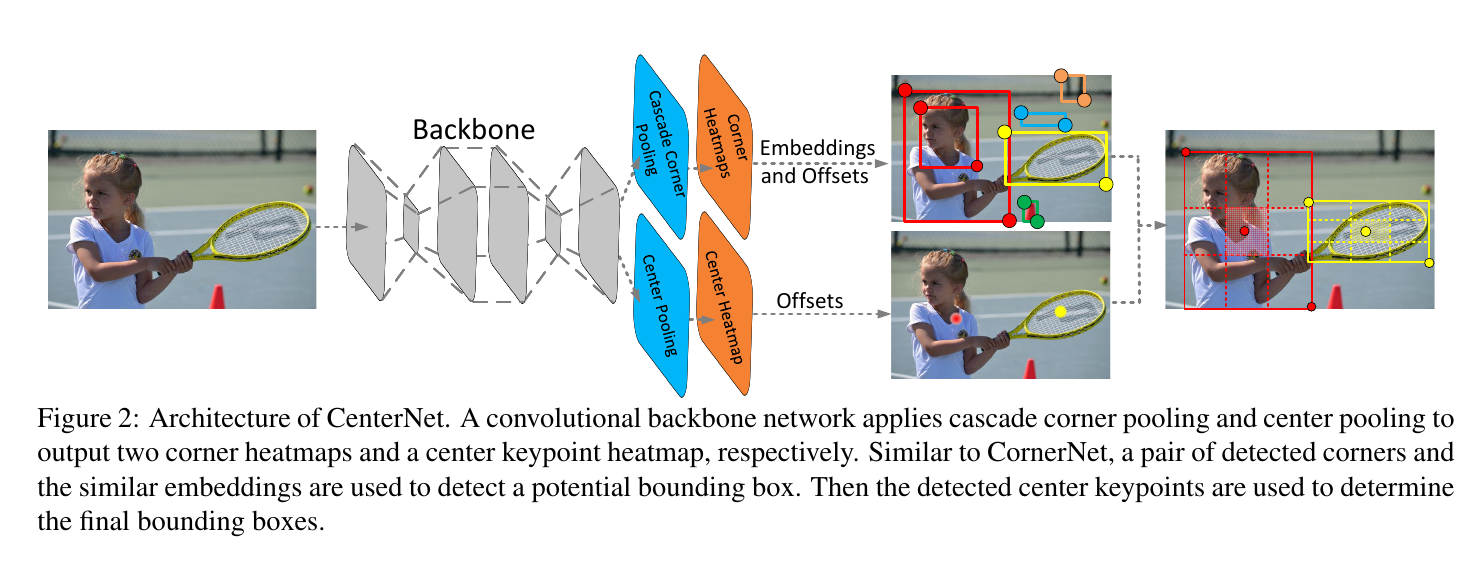
Center pooling and Cascade corner pooling
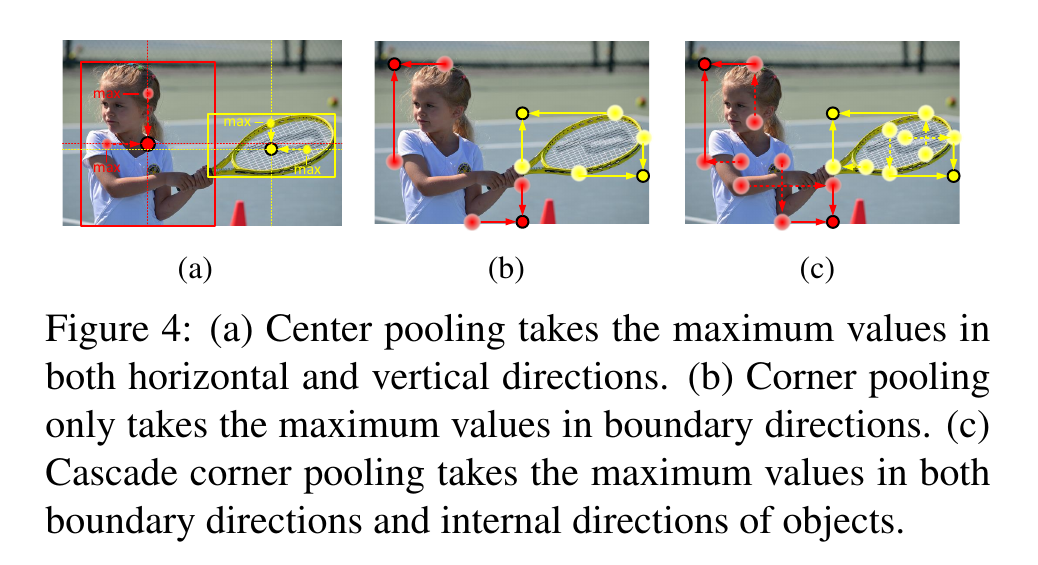 4 (a) is center pooling.
Cacade corner pooling basically means “go one step further” so it see more “in the box”.
4 (a) is center pooling.
Cacade corner pooling basically means “go one step further” so it see more “in the box”.
It first looks along a boundary to find a boundary maximum value, then looks inside along the location of the boundary maximum value2 to find an internal maximum value, and finally, add the two maximum values together. By doing this, the corners obtain both the the boundary information and the visual patterns of objects.
There’s an ablation study to show each of these three measures improves the performance.