Core idea
Predicts heat maps for top left and bottom right corner. Threshold and link them together by embedding. Also output the offset since convolution loses resolution.
The other parts of the paper is just “this is some new hotness so let’s use it”, which includes
- His own work for embeddings
- Hourglass
- Focal loss (RetinaNet)
Here’s the summary provided in CenterNet (Keypoint Triplets) paper:
For detecting corners, CornerNet produces two heatmaps: a heatmap of top-left corners and a heatmap of bottom-right corners. The heatmaps represent the locations of keypoints of different categories and assigns a confidence score for each keypoint. Besides, it also predicts an embedding and a group of offsets for each corner. The embeddings are used to identify if two corners are from the same object. The offsets learn to remap the corners from the heatmaps to the input image. For generating object bounding boxes, top-k left-top corners and bottom-right corners are selected from the heatmaps according to their scores, respectively. Then, the distance of the embedding vectors of a pair of corners is calculated to determine if the paired corners belong to the same object. An object bounding box is generated if the dis- tance is less than a threshold. The bounding box is assigned a confidence score, which equals to the average scores of the corner pair.
Corner pooling
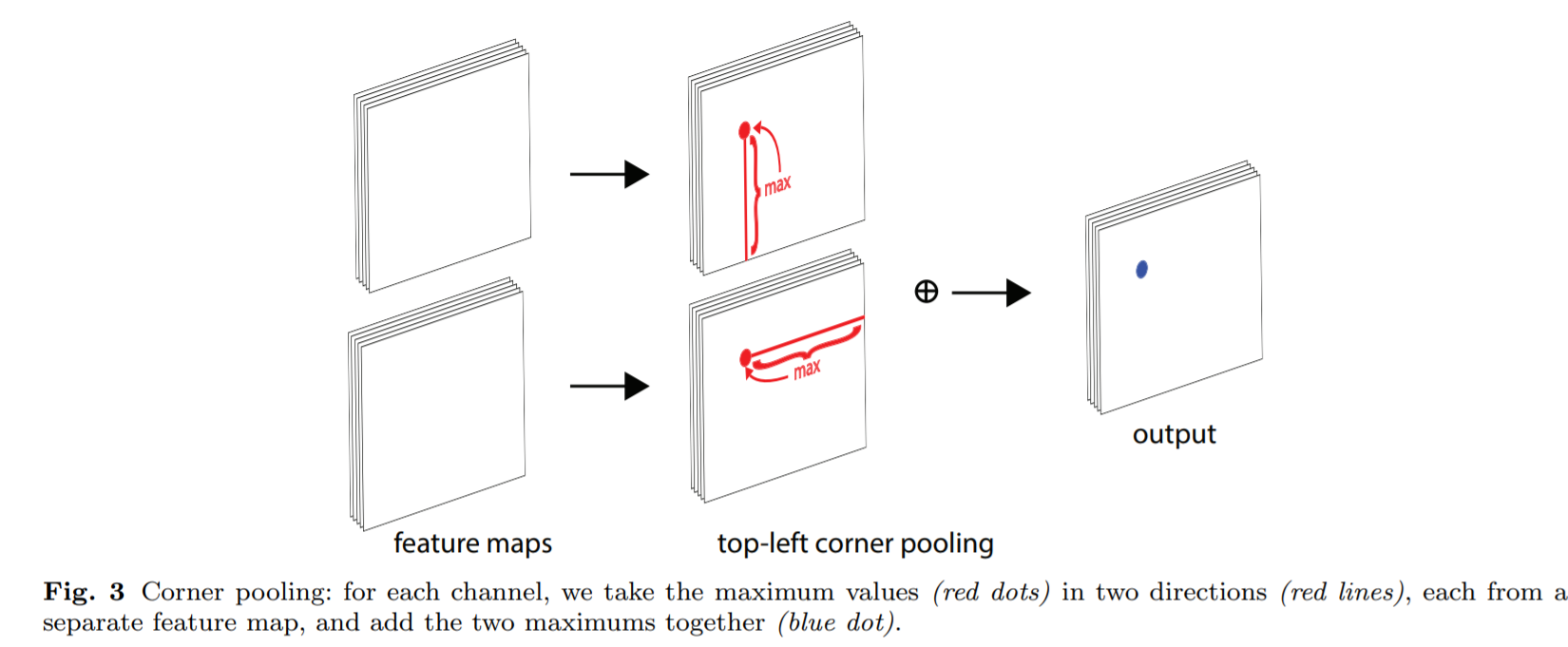
Where does the two feature map comes from? Why isn’t this generated from a single feature map? It’s not explained in the paper, kinda like why attention need to be generated from “key” and “value”.
The methods are mixed and matched together, and if something doesn’t improve the result, it’s just thrown out.