2021
Vision
Goal is to use multi camera to predict in BEV (What they call “3D vector space”).
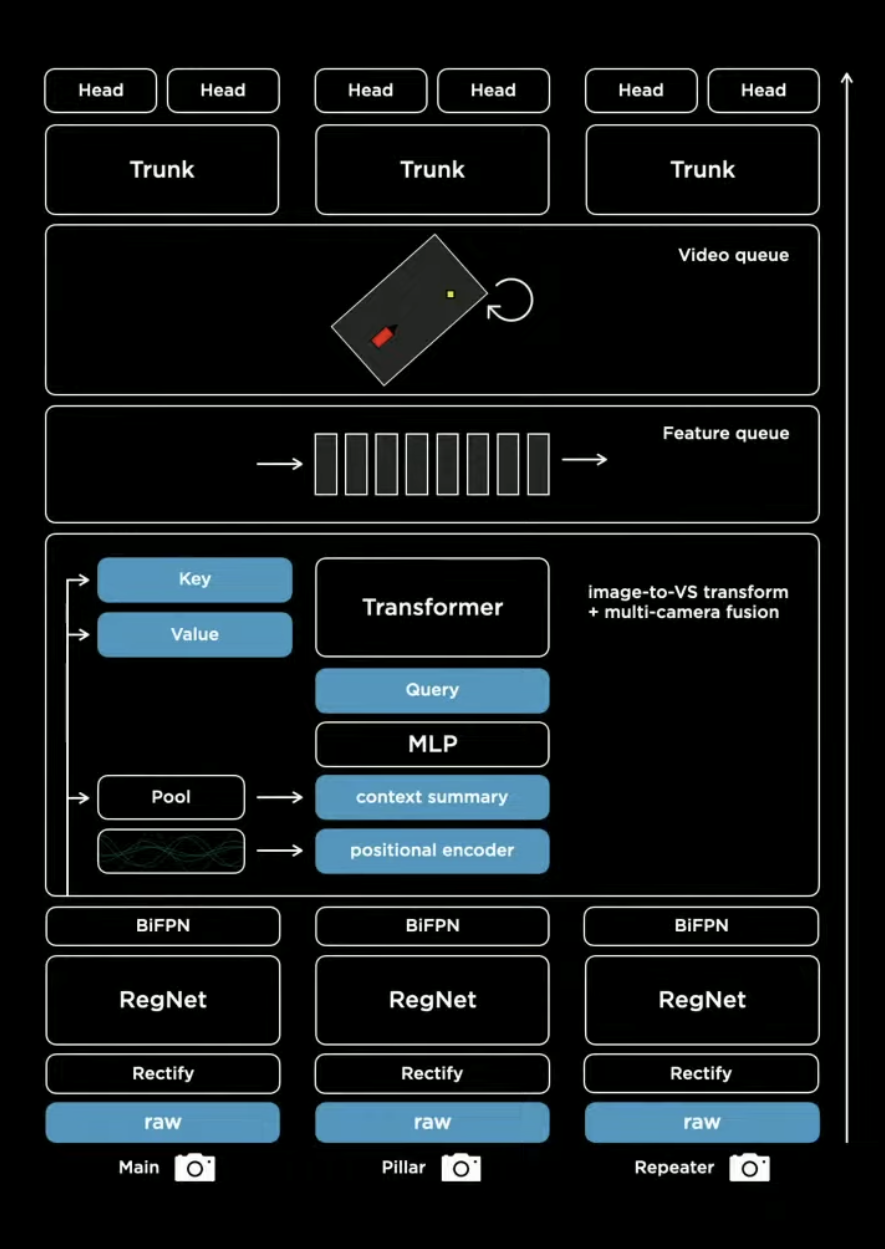 So we got a Hydra Net here with shared trunk and it outputs everything. That transformer basically transform images to BEV. It does not goes into detail to e.g. if it just query around certain pillar. A practical implementation can be found at BEVFormer.
The feature and video queue is a RNN. Specially, its hidden state is a raster, so in each state in the prediction we can constrain that only certain part of that is updated. The queue contains stuff that’s close in time and close in state.
So we got a Hydra Net here with shared trunk and it outputs everything. That transformer basically transform images to BEV. It does not goes into detail to e.g. if it just query around certain pillar. A practical implementation can be found at BEVFormer.
The feature and video queue is a RNN. Specially, its hidden state is a raster, so in each state in the prediction we can constrain that only certain part of that is updated. The queue contains stuff that’s close in time and close in state.
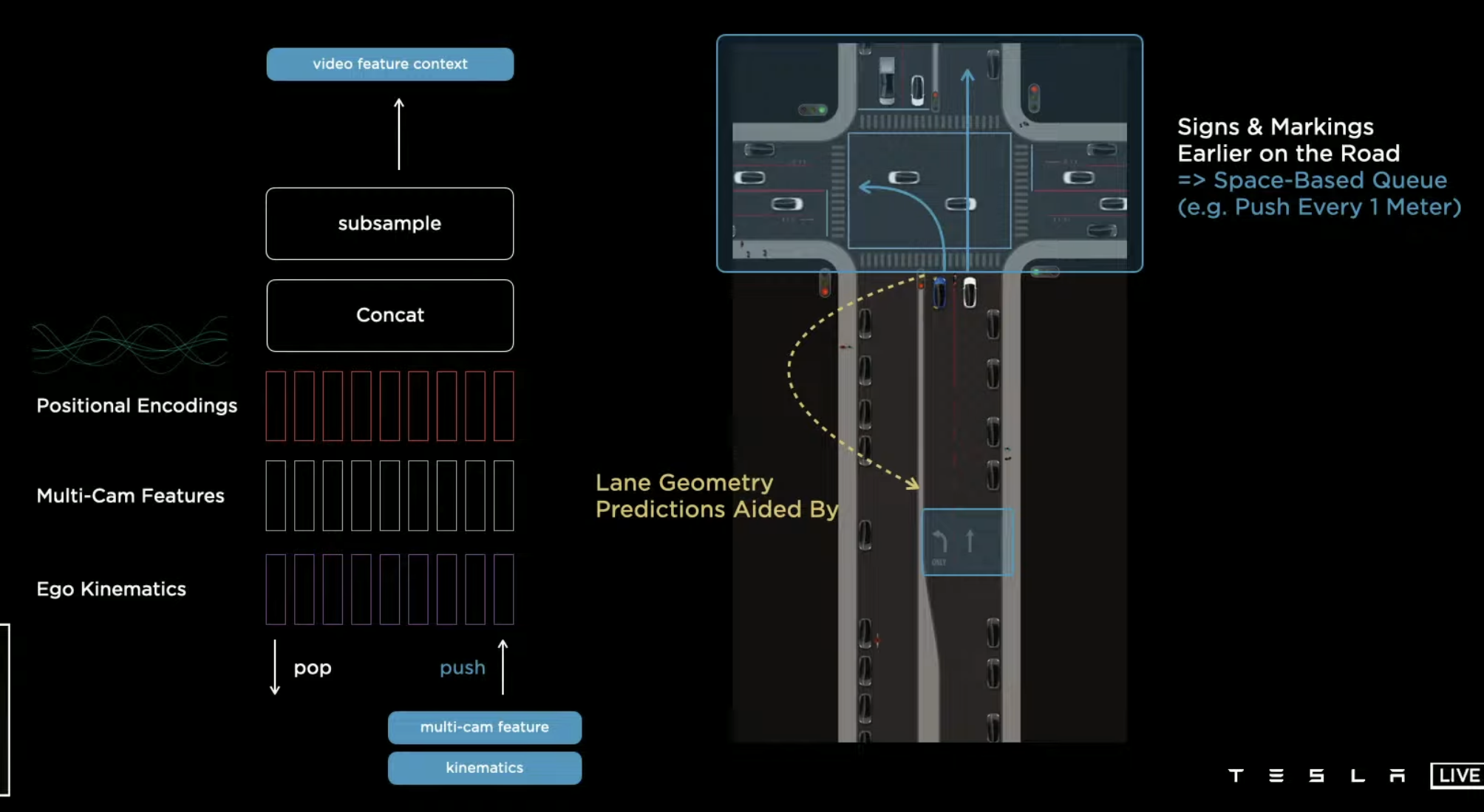
Labeling
They seem to use structure from motion output to get 3D points and label on them. With auto labeling too.
2022
Robot
Pretty standard. Most focusing on the hardware. Using 4 link joints instead of 2 links, etc. Does not cover much on the hand part. For the control part, still in the early stage. No fancy deep reinforcement learning etc., still talk about close loop control. Perception system seem overfitted on the tasks.
Planning
Trajectory generation with heuristics and neural networks with tree pruning and prioritization.
Perception
They got an occupancy net, which, strangely, does not use video model mentioned last year, and instead just align the frames using ego motion, just like BEVFormer. The output is occupancy grid in 3D. 10ms (how?) and no ray tracing. Unclear what’s the label / loss to train the model. Also talked about using NeRF to reconstruct the scene for unknown reasons.
They got another lane structure network. As Tesla does not use HD map, it need to infer these all from its perception system. That’s an interesting model that borrows idea from NLP with a autoregressive decoder.
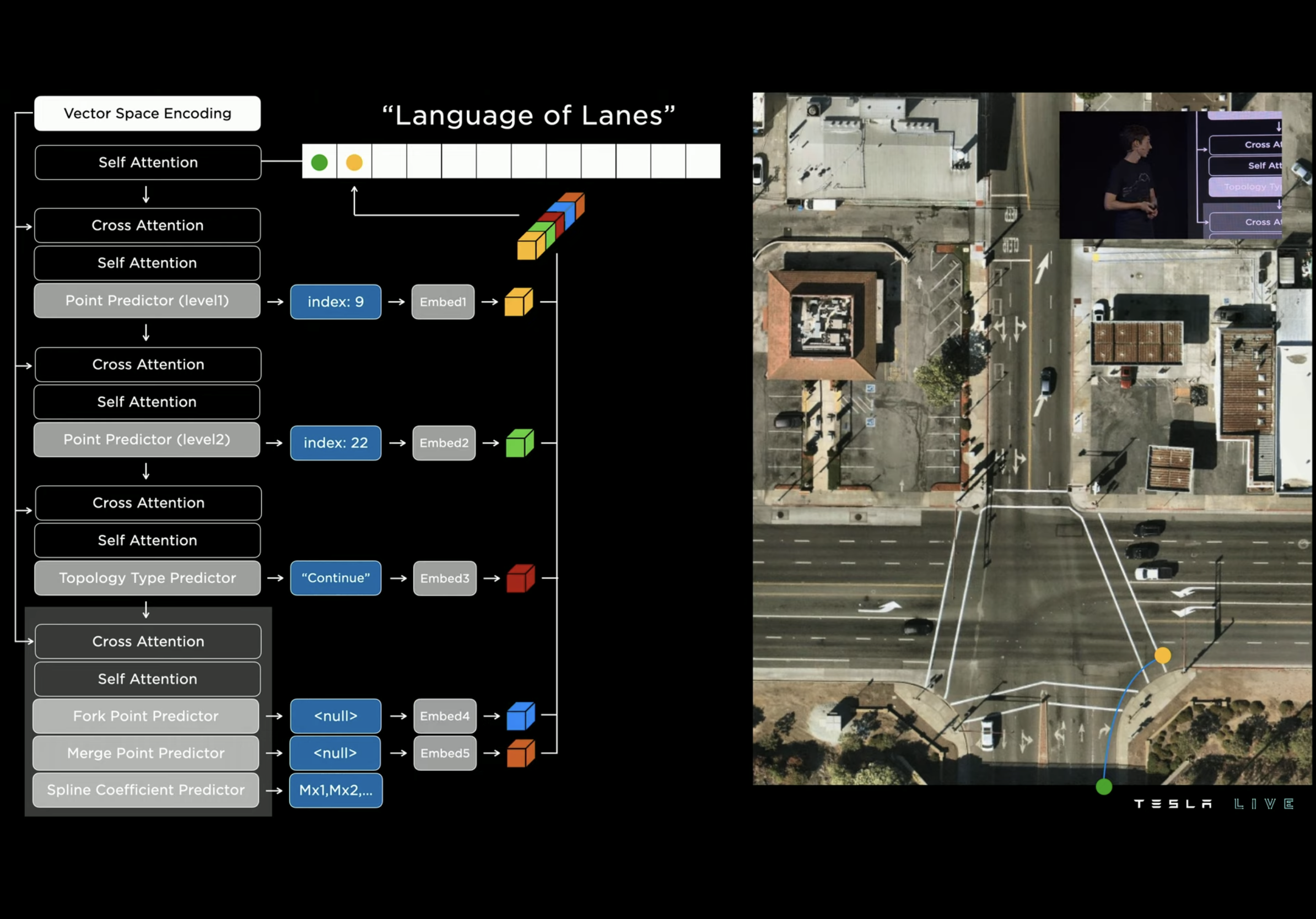 Divide the BEV into grids, and then do this thing, mapping nodes and relationships to languages. Results looks pretty good.
Divide the BEV into grids, and then do this thing, mapping nodes and relationships to languages. Results looks pretty good.
Through some optimization (they are using int8), all models run within 10ms. Pretty impressive considering that’s a lot of transformer.