The dual of Kalman Filter.
Instead of using moments to parameterize Gaussian, we use something called canonical parameterization.
The two are called the information matrix and information vector. The benefit is that we can represent log of Gaussian by a quadratic distance weighted by matrix , or, Mahalanobis distance.
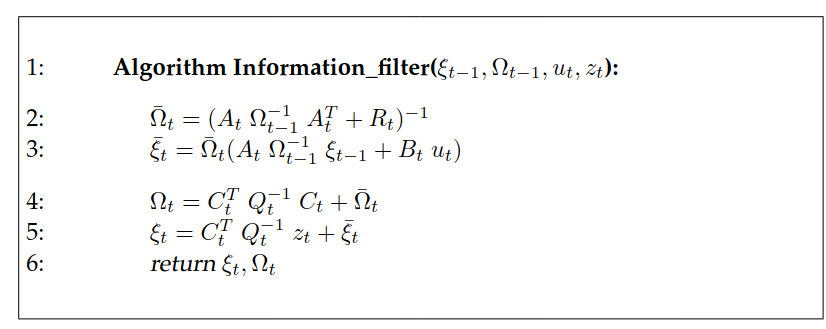
For the filter algorithm itself, what’s interesting is that compared with KF, the prediction step now needs matrix inverse. Previously it’s very simple. But in contrast, in the measurement update step it’s easier.